For months, the bond current market has flashed numerous warnings that a U.S. recession could be on the way, a look at that lots of in economic marketplaces have eventually recognized.
Just one of them is the 10-calendar year minus 3-month Treasury generate distribute, which has been beneath zero considering that late Oct, but has not been adverse for extensive plenty of to ship a definitive assertion about a pending economic contraction. Now Campbell Harvey, the Duke University finance professor who pioneered the use of that spread as a predictive device, reported the gauge may well be sending a “false sign, which is exciting for the reason that I’m the a single who invented the indicator.”
The astonishing conclusion from Harvey, whose 1986 dissertation at the University of Chicago connected the difference in between longer- and shorter-time period curiosity prices to upcoming U.S. financial growth, arrives at a time when the broader monetary market place has been fretting about a probable financial downturn in 2023.
On Tuesday, U.S. stocks
DJIA,
SPX,
managed to recuperate from four straight sessions of declines as buyers weighed recession fears and a shocking policy shift by the Bank of Japan. In just the bond market place, 41 diverse generate spreads had been unfavorable as of Tuesday, according to Dow Jones Marketplace Data — a signal of pessimism on the economic outlook.
The unfold in between premiums on the 3-month invoice
TMUBMUSD03M,
and 10-year be aware has been detrimental for just about two months — a reflection of a 10-year price buying and selling well beneath its 3-thirty day period counterpart — and concluded the New York session on Tuesday at minus 66.3 basis details. This kind of inversions have preceded eight out of the past eight recessions. The counterpart distribute between 2- BX:TMUBMUSD02Y and 10-12 months yields BX:TMUBMUSD10Y has been consistently below zero for pretty much six months, while it has emitted at least a single fake signal in the earlier, according to Harvey.
In an interview with MarketWatch, Harvey, a Canadian-born economist, said that one cause for his recent view is that the 3-month/10-calendar year distribute as a model “is so effectively identified now that it has impacted habits,” producing each companies and people to become more cautious — a type of “risk management” that “makes the likelihood of a smooth-landing a lot more very likely.”
“We’re in a period of time of slow advancement, which is dependable with the design, but as far as economic downturn, I’m skeptical of that. A hard landing is not likely,” he claimed by way of cellphone, though he did not rule out the likelihood of a gentle downturn. “What I’m indicating is uncomplicated. This is a worthwhile indicator and I imagine it is exact in forecasting slowing financial expansion. In terms of a tough landing, you will need to glance at other information.”
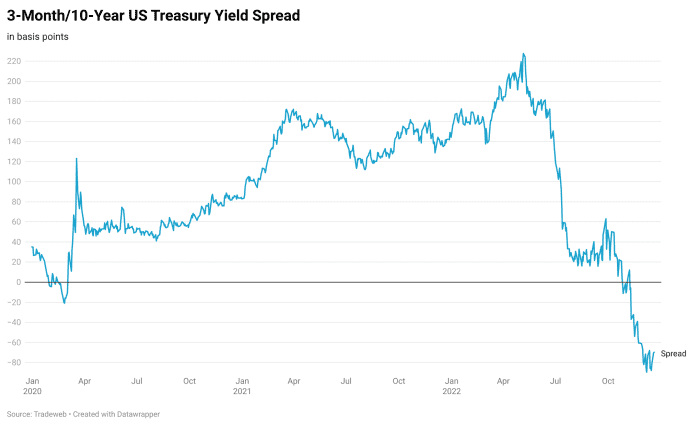
Resource: Tradeweb
Ordinarily, Treasury spreads must be widening and sloping upward, not downward, as buyers get into account brighter development prospective clients and request extra compensation for holding a bond or take note for a extended time period. They’ve been shrinking under zero, or inverting, as the Federal Reserve carries on to hike curiosity costs and investors aspect in the probable effect of these moves down the street.
On Oct. 26, the 3-thirty day period/10-yr distribute finished the U.S. buying and selling session below zero for the to start with time because March 2, 2020. At the time, Harvey said he would need to see the distribute stay down below zero by means of December to be confident that a economic downturn is on the way. It’s not nevertheless attained that marker, with a lot less than two weeks still left in the 12 months.
Listed here are the explanations the professor is now citing for why the unfold may not be as trustworthy an indicator of an approaching recession this time about, however it’s evidently pointing in the path of “lethargic” economic expansion:
- Unconventional work circumstance. Although unemployment is small ahead of every single recession, it is unconventional to have as a lot excess demand from customers for labor as the U.S. does now. “This means laid off workers can obtain function speedily.”
-
Engineering-driven layoffs. Laid-off personnel from organizations like Meta Platforms Inc.
META,
+2.28{21df340e03e388cc75c411746d1a214f72c176b221768b7ada42b4d751988996} ,
the parent of Fb, and Twitter “are hugely experienced and have pretty shorter period of unemployment,” in contrast to the 2007-2008 global monetary disaster and short 2020 COVID recession, which captured a broader established of staff from other industries. - Strong consumers and monetary institutions. People and the fiscal sector are stronger than they have been in advance of. That would make it less most likely that a drop in housing costs will induce a contagion, or that any troubles in the economical sector could distribute fast throughout the economic system, Harvey mentioned.
- Inflation-adjusted yields. Harvey focuses on inflation-modified yields simply because they better replicate the true financial outlook. “Once we inflation adjust the yields, the produce curve is not inverted — but it is flat (connected with lessen progress but not necessarily a economic downturn),” he said.
- Adjustments in behavior. Simply because of the inverted generate curve, organizations are not likely to “bet the firm” on a major investment project moreover shoppers are getting cautious and have lots of savings, in accordance to Harvey. “All of this potential customers to the self-fulfilling prophesy – i.e., decrease advancement. Having said that, you can also perspective it as possibility management. Even if expansion slows, providers can make it by means of devoid of massive layoffs.”








