The most deeply inverted section of the U.S. produce curve is a single that hasn’t despatched a bogus sign about the prospective clients of a U.S. economic downturn in extra than a 50 {21df340e03e388cc75c411746d1a214f72c176b221768b7ada42b4d751988996}-century of exploration.
That’s the distribute amongst 10-12 months and 3-thirty day period Treasury yields, which was all over 155.8 foundation factors below zero as of Wednesday — reflecting a 3-month T-bill price
TMUBMUSD03M,
that’s investing nicely earlier mentioned its 10-year counterpart
TMUBMUSD10Y,
The substantial distinction involving the two prices is pointing to the likelihood of a “deep recession,” according to Campbell Harvey, the Duke University professor who pioneered the use of the spread as an indicator of potential financial advancement.
Economic downturn fears are back again in target right after this week’s info presented new evidence that the Federal Reserve’s yearlong rate-hike cycle is eventually acquiring an impression on the labor market. Whilst bond-marketplace volatility has trended decreased about the previous 3 weeks, liquidity challenges and fears about a prospective U.S. debt-ceiling crisis continue on to plague Treasurys and exacerbate the market’s moves, according to Tom di Galoma, controlling director and co-head of charges investing for monetary expert services organization BTIG. The 10-12 months/3-thirty day period distribute is more under zero than it was in the operate-up to the 2007 -2008 economical crisis and in the late 1980s, when the Federal Reserve pushed fascination rates back previously mentioned 8{21df340e03e388cc75c411746d1a214f72c176b221768b7ada42b4d751988996} to 9{21df340e03e388cc75c411746d1a214f72c176b221768b7ada42b4d751988996}.
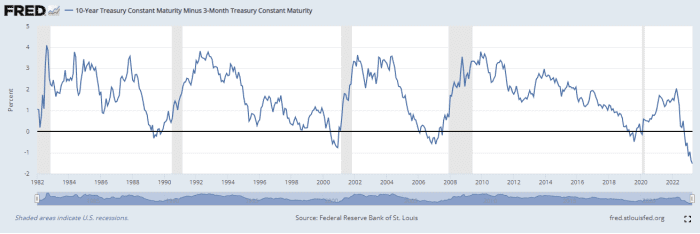
10-yr minus 3-month produce distribute as of April 4. Shaded locations show U.S. recessions.
Supply: Federal Reserve Financial institution of St. Louis
The measurement of the latest 10-yr/3-month inversion relative to where yields at present stand “is putting and amounts to a significant, really serious inversion,” Harvey explained by way of telephone on Wednesday. “The magnitude of the inversion can be instantly linked to a large slowdown in financial growth, and the model is predicting a deep recession.”
The unfold — which typically provides advance warning of a recession of any place from six to 18 months — initial fell under zero in Oct. In the beginning, Harvey held out hope that the U.S. could stay clear of a downturn. Past December, he explained to MarketWatch that the gauge — which hadn’t been inverted long sufficient at the time to send a definitive statement — may well be sending a “false signal” and that the likelihood of a smooth landing was additional possible.
That was in advance of the Federal Reserve hiked fees yet again in February and March, and the banking system more and more turned the channel by which the Treasury-curve inversion performed out in general public. Now policy makers have “gone way too considerably and are enjoying with hearth,” Harvey reported.
The curve is a line that plots the variations in yields throughout all credit card debt maturities. It normally slopes upward, with buyers demanding a top quality to compensate for dangers that can establish above time. A flatter curve can sign considerations about the financial outlook. An inverted curve, in which quick-dated yields rise above longer-dated yields, is a warning sign.
The inversion of the Treasury curve issues for a selection of causes. One particular of them is that it is upended the enterprise design employed by banking institutions, which make dollars by lending at bigger costs around the lengthier expression than they shell out borrowers for their deposits. An inverted produce curve helped sink California’s Silicon Valley Financial institution in March. “I have no plan how quite a few a lot more banking institutions the Fed has put at threat, but I undoubtedly hope they [policy makers] do,” Harvey said.
On Wednesday, Treasury yields completed generally reduce following weaker-than-anticipated private-sector career gains for March extra to concerns about a softening labor current market. In the meantime, important U.S. inventory indexes
DJIA,
SPX,
COMP,
also finished mostly reduced.
At Academy Securities in San Diego, David Gagnon, controlling director and head of U.S. Treasury trading, stated the money industry seems to be weighing two sets of “extreme situations.”
“For bonds, there’s a possibility that the economic climate will get caught in a recession,” Gagnon stated by means of cell phone. “Stocks are not much too nervous about the Fed obtaining to reverse training course in a economic downturn, and are in its place concerned that the economy does not go into recession,” leaving policy makers to continue to keep mountaineering premiums.
A modest part of the inversion in the 10-yr/3-month unfold is owing to technological components relating to supply imbalances, illiquidity, and concerns about the credit card debt ceiling, he said. The rest has to do with the bond market place “pricing in the threats of a hard landing and the Fed acquiring to answer aggressively.”








